A homegroup is a group of computers on a home network that can share files and printers. It is the feature introduced on Windows 7 onwards keeping the home users in mind. Using a homegroup makes sharing easier. You can share pictures, music, videos, documents, and printers with other people in your homegroup. Other people can't change the files that you share unless you give them permission to do so. You can help protect your homegroup with a password, which you can change at any time. In a simpler way we can say it is a home networking of group of computers present at home.
When you set up a computer with this version of Windows, a homegroup is created automatically. If a homegroup already exists on your home network, you can join it.
After you create or join a homegroup, you select the libraries that you want to share. You can prevent specific files or folders from being shared, and you can share additional libraries later.
Computers must be running Windows 7 to participate in a homegroup. HomeGroup is available in all editions of Windows 7.
Note:
In Windows 7 Starter and Windows 7 Home Basic, you can join a homegroup, but you can’t create one.
Step 1. Create a homegroup
Open HomeGroup by clicking the Start button , clicking Control Panel, typing homegroup in the search box, and then clicking HomeGroup.
On the Share with other home computers running Windows 7 page, click Create a homegroup, and then follow the instructions.
Step 2. Add your other computers to the homegroup
After someone on your home network creates a homegroup, the next step is to join it. You'll need the homegroup password, which you can get from the person who created the homegroup.
Open HomeGroup by clicking the Start button , clicking Control Panel, typing homegroup in the search box, and then clicking HomeGroup.
Click Join now, and then complete the wizard.
Step 3. Access homegroup files
Computers that belong to your homegroup will appear in Windows Explorer.
To access files or folders on other homegroup computers
1. Click the Start button , and then click your user name.
2. In the navigation pane (the left pane), under Homegroup, click the user account name of the person whose files you want to access.
3. In the file list, double-click the library you want to access, and then double-click the file or folder you want.
Step 4. Control which files or folders are shared with your homegroup
When you created or joined your homegroup, you selected the libraries you wanted to share with other people in the homegroup. Libraries are initially shared with Read access, which means that you can look at or listen to what's in the library, but you can't make changes to the files in it. You can adjust the level of access later, and you can exclude specific files and folders from sharing.
Step 5: Share printers
Printers that are connected with a USB cable can be shared with a homegroup. After the printer is shared, you can access it through the Print dialog box in any program, just like a printer that's directly connected to your computer.
To share your printer with the homegroup
1. Open HomeGroup by clicking the Start button , clicking Control Panel, typing homegroup in the search box, and then clicking HomeGroup.
2. Click Install printer.
3. Select the Printers check box, and then click Save changes.
To automatically connect to a homegroup printer
-Click the Windows found a homegroup printer message that appears.
To manually connect to a homegroup printer
1. On the computer the printer is physically connected to, click the Start button , click Control Panel, type homegroup in the search box, and then click HomeGroup.
2. Make sure the Printers check box is selected.
3. Go to the computer you want to print from.
4. Open HomeGroup by clicking the Start button , clicking Control Panel, typing homegroup in the search box, and then clicking HomeGroup.
5. Click Install printer.
6. If you don't already have a driver installed for the printer, click Install driver in the dialog box that appears.
Check here for MS official guide along with video...
This is where the sharing of knowledge starts. The windows administrators, end user computing specialists, Desktop deployment architect and virtualization enthusiast by profession or who aspiring this profession can follow this blog and share your thoughts...
Search on this Blog
Apr 14, 2011
Apr 4, 2011
Microsoft Launches – MVA (Microsoft Virtual Academy)
Microsoft is launched a new learning experience for you called MVA (Microsoft Virtual Academy) with the objective of helping you to build the necessary skills to grow in your IT role and career with Microsoft Cloud technologies.
This Microsoft Virtual Academy will help you improve your IT skill set and thus advance your career with a free, easy to access training portal that allows you to learn at your own pace, focusing on Microsoft technologies. Earn points, each completed trainings and get recognized by the community by moving up the ladder into a Bronze, Silver or Platinum membership.
In MVA, you will find the following resources learning content such as:
Register now! Visit this site http://www.microsoftvirtualacademy.com/ and follow the registration process.
This Microsoft Virtual Academy will help you improve your IT skill set and thus advance your career with a free, easy to access training portal that allows you to learn at your own pace, focusing on Microsoft technologies. Earn points, each completed trainings and get recognized by the community by moving up the ladder into a Bronze, Silver or Platinum membership.
In MVA, you will find the following resources learning content such as:
- Whitepapers
- Webcasts
- Training Videos
- Forums
- Access to community experts
- Statistics of your performance and professional progress
- Level of knowledge within the career selected.
Register now! Visit this site http://www.microsoftvirtualacademy.com/ and follow the registration process.
Labels:
Microsoft application virtualization,
MVA
Mar 24, 2011
Windows XP to Windows 7 Migration Guide
This guide walks you through the decisions you'll make when migrating from a Windows XP environment to Windows 7, and learn about the tools and resources available from Microsoft to help you each step along the way.
There are three major steps we need to consider while getting into XP to windows 7 migration.



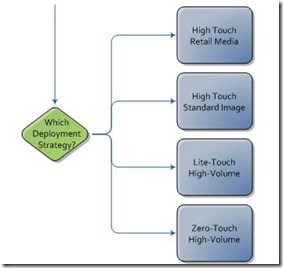
There are three major steps we need to consider while getting into XP to windows 7 migration.
- Collect, Analyze, and Test
- Remediate Applications – Fix
- Remediate Applications – Virtualize (Optional)
- Deploy Operating System
Collect, Analyze, and Test
This section walks you through how to collect information about running your hardware and applications. It then analyzes the list of applications in the environment, and then test those applications for compatibility.
Remediate Applications – Fix
After the collection and analysis of data, we must test and mitigate (fix) the application issues. This process can be accomplished by using the Standard User Analyzer (SUA), the Compatibility Administrator, and the Setup Analysis Tool. All tools are available with the Microsoft Application Compatibility Toolkit (ACT).
Remediate Applications – Virtualize (Optional)
Virtualization may help to solve an incompatibility problem. There are several ways to virtualize applications. We can run virtual machines on centralized servers, distribute them to new physical desktops and/or combine the deployment of a new operating system with virtualized applications. In this section, we’ll find material that will help you to determine which option works best for us.
Deploy Operating System
Once we have determined our software is compatible, we can start the deployment process. Please be aware that there is no upgrade path from Windows XP to Windows 7, only from Windows XP to Windows Vista and then Windows Vista to Windows 7. We can, however, use the User State Migration Tool (USMT) to keep the data in place and re-deploy just the Operating System.
Here you will find complete Microsoft guide
Mar 23, 2011
Microsoft’s Virtualization Solutions
Virtualization is one of the most effective methods to save costs, increase the availability , and improve agility within an organization’s infrastructure. Microsoft Virtualization solutions provide you with the way to optimize your infrastructure by helping IT provide the services more rapidly and efficiently while allowing an organization to consume these services more effectively in a dynamically changing business climate. Click here to read more….
Virtualization Introduction…..
MAP Assessment Tool…
Creating a Viable Virtualization Design
Overview on MED-V
Resources
One point where in you have access to White Papers, Videos, Virtualization TechNet Resources, Virtualization Tools (ROI Calculator, Microsoft Assessment and Planning (MAP) Toolkit and HyperGreen Tool) and MS Virtual Labs. Click here to access the resources....Microsoft Virtualization Demos
Learn more about the Microsoft Virtualization products and solutions, and see them in action by viewing this collection of demos.Virtualization Introduction…..
MAP Assessment Tool…
Creating a Viable Virtualization Design
Overview on MED-V
Microsoft Virtualization Community
To join the Virtualization conversation. Follow Microsoft experts to stay up-to-date on the latest industry and Microsoft Virtualization news and information. Click here to join community…Mar 18, 2011
Internet Explorer 9 Product Guide and Group Policy Reference…
Windows Internet Explorer 9 (abbreviated as IE9) is the new version of the Internet Explorer web browser from Microsoft. It was released to the public on March 14, 2011.
System requirements for IE9:
Windows 7
Windows Server 2008 R2,
Windows Server 2008 (with Service Pack 2(SP2)
Windows Vista,
Windows Server 2008
Note: Both 32-bit, 64-bit builds are supported and Windows XP is not supported.
Overview for IT Professionals:
Internet Explorer 9 can also help IT pros standardize on the only web browser that provides nearly 1,500 Group Policy settings to help streamline desktop management and support. IT pros can have trouble gaining user acceptance for a web browser that end users do not like. Internet Explorer 9 can help alleviate this issue. The browser includes features that end users have specifically requested, such as tear-off tabs, the Download Manager, and better integration with the Windows 7 taskbar. Internet Explorer 9 is also considerably faster than Internet Explorer 8. End users who enjoy Internet Explorer 9 can drive adoption, helping you to reduce management and support costs by standardizing the desktop. Click here to read more.
FAQ for IT Professionals:
Find information about new features in Internet Explorer 9 that are important to IT Professionals. Click here for checking out for Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Internet Explorer 9 Product Guide:
This product guide outlines new features in Internet Explorer 9, highlights the top features, and provides additional information on features specific for end users, developers, and IT professionals. Read on to learn more about how Internet Explorer 9 unlocks the Beauty of the Web. IT Professionals and IE9 enthu’s download product guide here.
Group Policy Settings Reference Windows IE9:
The policy settings included in this spreadsheet cover Internet Explorer 5, Internet Explorer 6, Internet Explorer 7, Internet Explorer 8 and Internet Explorer 9. These files are used to expose policy settings when you edit Group Policy objects (GPOs) using Group Policy Object Editor (also known as GPEdit). Download the reference spreadsheet here.
System requirements for IE9:
Windows 7
Windows Server 2008 R2,
Windows Server 2008 (with Service Pack 2(SP2)
Windows Vista,
Windows Server 2008
Note: Both 32-bit, 64-bit builds are supported and Windows XP is not supported.
Overview for IT Professionals:
Internet Explorer 9 can also help IT pros standardize on the only web browser that provides nearly 1,500 Group Policy settings to help streamline desktop management and support. IT pros can have trouble gaining user acceptance for a web browser that end users do not like. Internet Explorer 9 can help alleviate this issue. The browser includes features that end users have specifically requested, such as tear-off tabs, the Download Manager, and better integration with the Windows 7 taskbar. Internet Explorer 9 is also considerably faster than Internet Explorer 8. End users who enjoy Internet Explorer 9 can drive adoption, helping you to reduce management and support costs by standardizing the desktop. Click here to read more.
FAQ for IT Professionals:
Find information about new features in Internet Explorer 9 that are important to IT Professionals. Click here for checking out for Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Internet Explorer 9 Product Guide:
This product guide outlines new features in Internet Explorer 9, highlights the top features, and provides additional information on features specific for end users, developers, and IT professionals. Read on to learn more about how Internet Explorer 9 unlocks the Beauty of the Web. IT Professionals and IE9 enthu’s download product guide here.
Group Policy Settings Reference Windows IE9:
The policy settings included in this spreadsheet cover Internet Explorer 5, Internet Explorer 6, Internet Explorer 7, Internet Explorer 8 and Internet Explorer 9. These files are used to expose policy settings when you edit Group Policy objects (GPOs) using Group Policy Object Editor (also known as GPEdit). Download the reference spreadsheet here.
Labels:
"IE 9 FAQs",
"IE9 Group Policy",
"internet Explorer 9",
"New Browser",
FAQ,
IE9
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)
